The optimal irrigation
How does the water balance of the soil work?
Plants absorb water and nutrients through their roots, especially in the zone where most of the fine roots are located. In the garden, these fine roots are usually found at a soil depth of 10–60 cm (depending on the plant). Of course, there are plants that root several meters deep, but this is usually not relevant for gardens and will not be further discussed here.
Why is the root zone important for irrigation?
- Water uptake: Plants absorb water through their fine roots.
- Nutrient Availability: Nutrients in the soil are only absorbed in dissolved form. Therefore, the root zone must be sufficiently moist so that nutrients can be dissolved and accessed by the roots.
- Soil Properties: The storage capacity, drainage, and air circulation in the root zone determine how much water is available to the plants before the soil becomes dry or waterlogging occurs.
- Plant Growth: Dryness or waterlogging in the root zone can inhibit root growth and make the plant susceptible to stress. Therefore, balanced moisture is essential.
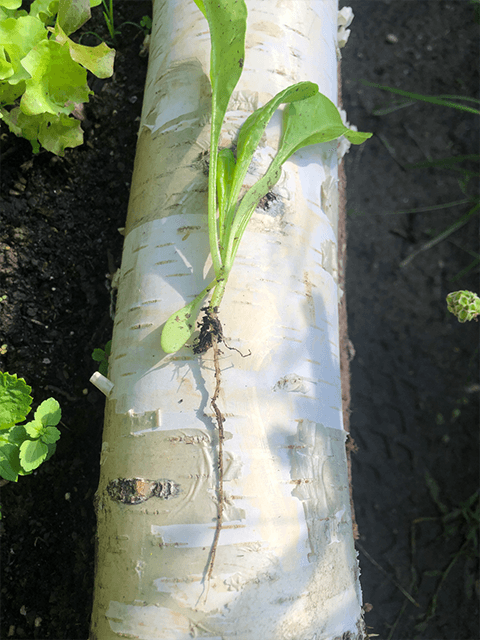
At the root of a young chard plant, you can see beautifully how quickly roots grow:

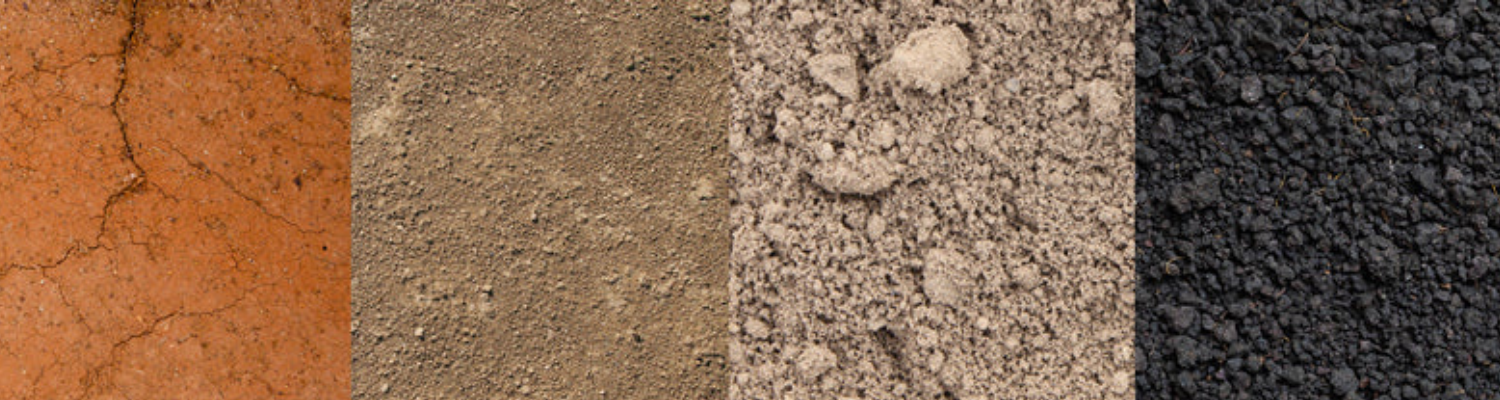
The soil types
Soil predominantly (>90%) consists of mineral components of varying grain sizes and an organic matter content (<10%).
Mineral components and their grain sizes
The mineral components of the soil are classified according to their grain size:
Sand: Grain size: 0.063–2 mm
Silt: Grain size: 0.002–0.063 mm
Tone: Grain size: < 0.002 mm
In practice, almost only mixed forms occur, which are referred to as loam. The classification is done using the soil triangle, which represents the mixing ratios. For example:
Sandy Loam: 60 % sand, 30 % silt, 10 % clay
Clayey Soil: 35% Clay, 40% Silt, 25% Sand

clay
Due to the small grain size, clay binds water very strongly. Highest water storage capacity, but not fully usable for plants due to the strong binding. Low percolation, risk of soil compaction and waterlogging.
Clay soils are difficult to work with for agricultural purposes, but very fertile when well-aerated. Clay soils are widespread in Europe.
silt (or silt)
Clay soils have good water retention, which is beneficial for plants with higher moisture requirements. Rich in minerals and provides a good nutrient base. Prone to sealing, crusting, and compaction.
Suitable for vegetables such as potatoes, cabbage, spinach, and beetroot, flowering plants like asters, phlox, and bellflowers, and fruits like apple and cherry trees that prefer consistent moisture.
sand
In sandy soils, water drains quickly, they have a low water retention capacity, and nutrients are easily washed out. They require more frequent irrigation, but in smaller amounts.
Sandy soils are well-suited for plants that prefer dry conditions and are sensitive to waterlogging due to their good drainage, loose structure, and quick warming. This includes, for example, herbs and Mediterranean plants such as lavender and rosemary, coneflower, carrot, and radish.
loam
Good balance between water retention capacity and drainage. Clayey soils store enough water for plants, but they do not tend to become waterlogged like clay soils. Due to their high nutrient retention and loose structure, clayey soils are suitable for almost all types of plants. Clayey soils are optimal for cereal cultivation (wheat, barley), vegetables (potatoes, onions), and fruit orchards.
What properties do the soil types have?
1. Sandy soils
Organic material content: 1–2 %
Description: Sandy soils have a low ability to store organic material, as they have a low surface area and poor nutrient retention. Organic substances are broken down and leached away more quickly.
Water storage:
Low fertility
Low water storage capacity, rapid water loss
Improvement through the addition of humus or compost is necessary
Plants often have only a short time access to water.
Suitable Irrigation: Frequent but small waterings to maintain surface moisture.
2. Silty soils
Organic material content: 2–4 %
Description: Silt soils have a medium structure that allows for moderate storage of organic material. They promote even decomposition of organic substances.
Characteristics:
Good water storage capacity
Average fertility
Sensitive to erosion by wind and water, therefore mulch or organic cover layers are recommended.
Suitable Irrigation: Even irrigation with moderate amounts
3. Clay soils
Organic material content: 3–6 %
Description: Clay soils offer the best combination of water retention, nutrient availability, and decomposition rate. They promote the formation and storage of humus.
Characteristics:
Suitable Irrigation: Medium-sized water applications at larger intervals. Flexible, both longer dry periods and a lot of water are generally well tolerated.
4. Clay soils
Organic material content: 2–5 %
Description: Clay soils retain organic substances well due to their fine particles, but the slow air exchange can hinder decomposition, especially in waterlogging.
Characteristics:
Suitable Irrigation: Longer, slow irrigation with small amounts of water to achieve uniform moisture.
5. Peat soils (special case)
Organic material content: 30–90 %
Description: Peat soils consist mainly of organic material, as decomposition is greatly slowed under water-saturated conditions.
Characteristics:
Very high water storage capacity
Nutrient-poor, as organic substances are hardly decomposed.
Extremely low in oxygen, therefore mostly unsuitable for agriculture.
Valuable CO2 Storage
Field capacity and wilting point: The water storage capacity of the soil
Two central terms in the water balance of the soil are field capacity and wilting point.
- field capacity
Field capacity describes the maximum amount of water that the soil can retain after a rain, without excess water draining away. - Which point
The wilting point is the condition at which the soil contains so little water that plants can no longer absorb water and begin to wilt.
'The area between field capacity and wilting point is available as water for the plants and is referred to as plant-available water.'
Relationship between soil type and field capacity
The following overview table shows the field capacity, the wilting point, and the plant-available water (PAW) for different soil types. The values are averages, as they depend on factors such as organic content, soil structure, and compaction:
Field capacity and wilting point
|
soil type |
Field capacity (% Volume) |
Which point (% Volume) |
Plant-available water (PAW) (% Volume) |
comments |
|
sandy soil |
5–15 |
1–5 |
4–10 |
Very low water retention capacity, water drains away quickly. Irrigation often necessary. |
|
silty soil |
20–35 |
7–15 |
13–20 |
Good water storage capacity, but sensitive to erosion. |
|
Loamy sand |
15–25 |
5–10 |
10–15 |
Improved water retention compared to pure sand. |
|
clay soil |
30–45 |
10–20 |
20–25 |
Optimal soil for agriculture, balanced storage and drainage properties. |
|
Toniger loam |
35–50 |
15–25 |
20–25 |
High water retention, but potentially slow drainage. |
|
The sound booth |
40–60 |
20–30 |
15–30 |
High water storage capacity, but water for plants is less available as it is strongly bound. |
|
Moorish Bodies |
70–90 |
30–50 |
40–60 |
Extremely high water retention due to organic substances, nutrient deficiency is often a problem. |
Organic substances (humus)
Organic substances, such as dead plant material, roots, and microorganisms, are called humus. Humus is constantly decomposed by microorganisms in the soil and thus transformed into plant food.
- Humus improves water retention, soil structure, and nutrient availability.
- Organic substances contribute to the formation of macro- and micropores, which are important for water and air circulation.
- Soils with high humus content can store more plant-available water.

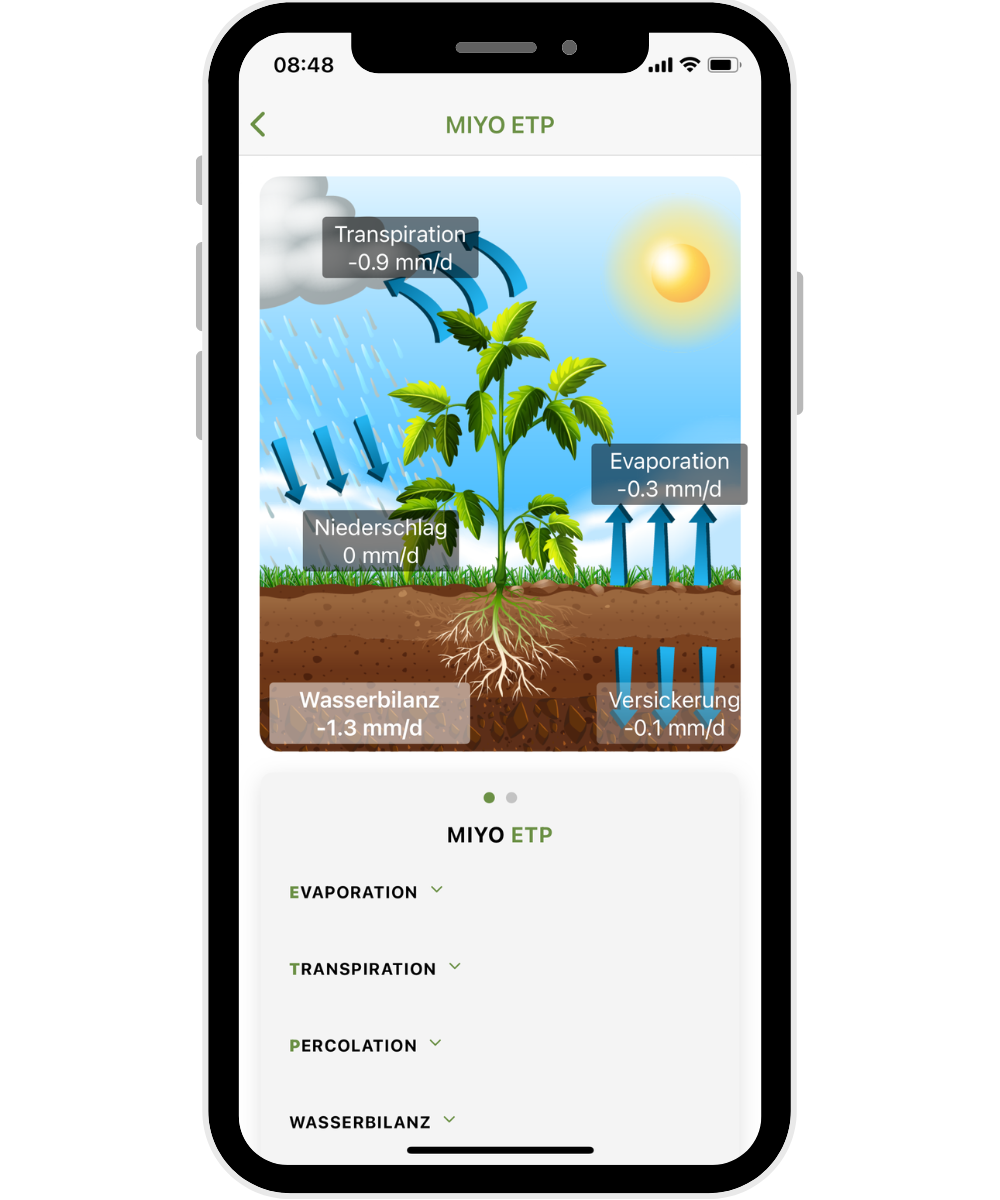
What is evapotranspiration?
Evapotranspiration consists of evaporation (water evaporation from the soil) and transpiration (water release by plants). These processes, together with infiltration, determine how quickly water is lost from the root zone.
Factors that influence evapotranspiration
- Climate: High temperatures, direct sunlight, dry air, and wind accelerate water evaporation.
- Ground Cover: Dense vegetation reduces direct soil evaporation but increases transpiration.
- Soil: Sandy soils dry out faster, while clay soils retain water longer.
What are typical evapotranspiration values
Evapotranspiration per week in Central Europe in spring and autumn ranges between 4mm and 20mm and rises in summer to 15mm to 50mm. 1mm corresponds to one liter of water/m². This water loss must be compensated by rainfall or irrigation to ensure that the plants are adequately supplied. The large fluctuations in evapotranspiration should be taken into account in irrigation.
How does MIYO calculate evapotranspiration
MIYO calculates the evapotranspiration for each of your irrigation cycles based on the weather data of the location, the entered soil type, and the solar intensity and soil moisture measured by the Sensor.
Tips for Sustainable Irrigation
- Consider soil type: Sandy soils often require more frequent but smaller waterings, while clay soils can tolerate larger, less frequent amounts of water. With MIYO, all irrigation parameters can be set according to specifications and individually adjusted to meet the garden's needs.
- Monitor Evapotranspiration: MIYO accurately calculates the evapotranspiration for each irrigation circuit based on measured and transmitted data. This allows the irrigation to precisely compensate for water losses due to evaporation and transpiration.
- Optimize Irrigation Timing: Watering early in the morning, before it gets hot, reduces water loss through evaporation. The afternoon is also an option. Avoid watering in the evening or at night, as prolonged moisture on leaves can promote the growth of fungal diseases. In the MIYO app, you can adjust the times with just a few clicks for each day.
- Drip irrigation: This method delivers water directly to the plant roots and minimizes losses due to evaporation.
- Mulching: reduces evaporation and ensures that water stays longer in the root zone.
- Avoid Overwatering: Waterlogging causes serious and long-term damage to plants and soil and should therefore be avoided at all costs. The easiest way to do this is with a smart MIYO irrigation system. In any case, irrigation computers with fixed intervals should be avoided, as they will inevitably lead to constant over- or underwatering.
- Adjust irrigation intervals to the plant: Shallow-rooted crops benefit from more frequent watering. Deep-rooted plants need water less often, but in larger quantities, to moisten the deeper layers. These parameters can be easily adjusted to the needs of the plant in the MIYO app.
- Measuring soil moisture: Soil sensors or simple grab tests can help monitor moisture in the root zone and avoid overwatering or drought stress.
- Increase water retention capacity: Organic matter (e.g. humus) in the root zone improves water storage capacity and increases the amount of water available to plants.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between field capacity and wilting point?
Field capacity describes the maximum amount of water that the soil can retain, while the wilting point defines the condition in which plants can no longer absorb water.
2. How can I determine the water needs of my plants?
The water requirement depends on evapotranspiration, soil type, and plant type. Soil sensors help to determine the need precisely.
3. Which soil types store water best?
Clay soils have the best combination of water absorption and storage, while loamy soils can hold a lot of water but make it poorly available.
4. How can I calculate the water needs of my plants?
The water requirement depends on evapotranspiration, soil type, and plant species. A rule of thumb is to multiply the daily evapotranspiration (in millimeters) by the cultivation area. MIYO calculates the water requirement based on entered parameters, the values measured by the soil moisture sensor, and weather data from the internet.
5. How do I know if the soil is too dry or too wet?
Too dry: The plants begin to wilt, and the soil feels crumbly and hard.
Too wet: Water collects on the surface, or the soil feels muddy (especially in clay soils). The MIYO soil moisture sensor is an accurate method to monitor moisture and determine irrigation needs.
The key to a healthy garden is the right soil moisture. Not too dry, but not too wet for extended periods. You should definitely avoid overwatering, as this leads to soil compaction and valuable nutrients being washed away. Therefore, a timed irrigation system must be continuously adjusted to seasonal and weather conditions. Thus, we recommend using the MIYO moisture sensor in sensitive garden areas.
"This is how you control your intelligent irrigation with MIYO"
"Divide your garden into irrigation zones. Areas with similar water needs can usually be grouped together in one zone. Later changes and reassignments of sensors and valves can be easily carried out with MIYO."
To save water, it is best to plant plants with similar water needs in one area. The Sensor should be placed at a representative location in this area. Targeted water supply, e.g., drip irrigation, is more economical than watering large areas, e.g., with sprinklers. The irrigation should be designed so that the area is supplied evenly.
MIYO can water either purely time-controlled or with soil moisture measurement. Even with watering using soil moisture measurement through the Sensor, you can enter time windows during which watering can take place. In the watering settings, you can set the lower and upper limits of moisture. To achieve natural fluctuations and save water, make sure to set the moisture limits far enough apart. It usually does not need to be watered every day.
The consideration of rain and rain forecast can be set optionally for both time-controlled and sensor-controlled circuits.
You can adjust the irrigation to the water consumption of the plants in the irrigation settings of the circle in the MIYO app. There are no universally applicable guidelines; instead, the values must be determined individually for plants and gardens. In addition to the type of plants, factors such as location, sun orientation, wind exposure, type of planting, and soil quality of the garden should also be considered. The more resistant a plant is to drought, the lower the lower limit of the soil moisture measured by the MIYO Sensor can be set. With the numerous adjustment options, the intelligent MIYO irrigation can be equally well adapted for flowers and vegetables as for lawns and trees.
Use mulch: Adding a layer of mulch around your plants helps conserve soil moisture by reducing evaporation. Mulch also helps suppress weed growth, regulate soil temperature and improve soil structure in the long term.
MIYO is the best guarantee for optimal water supply to your garden and for preventing overwatering. Adjustments to the growth phases of the plants or observations of plant health can be done easily on your phone.
"Switch now and let your smart MIYO irrigation system do the work for you."

